Introduction to Home Plumbing Systems
Plumbing is one of the most essential components of any home, silently ensuring comfort and convenience in everyday life. A solid understanding of your home’s plumbing system is invaluable, especially for maintenance and prompt troubleshooting. Whether you are looking to prevent common problems or just want to know how your home ticks, grasping these basics makes a world of difference. If you are seeking professional solutions or need an inspection, affordable plumbing in Westminster offers reliable local service and expertise.
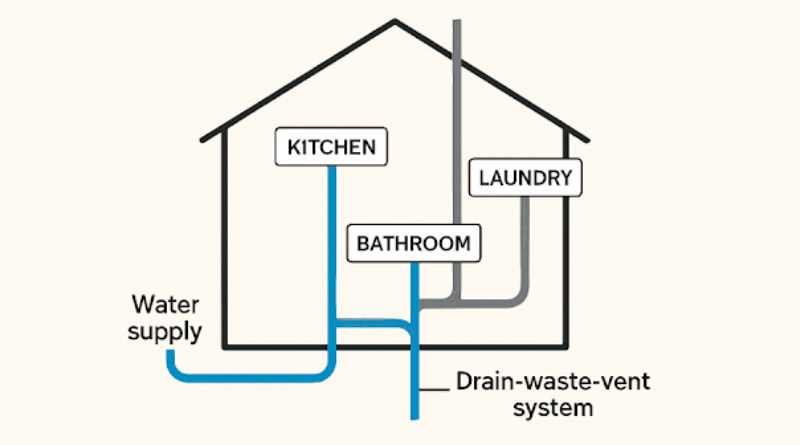
Home plumbing consists primarily of two major subsystems: the water supply system and the drain-waste-vent (DWV) system. Learning how these systems are arranged and what their parts do helps not only with DIY fixes but also with communicating your needs to plumbers and contractors when issues arise.
The typical water supply system delivers clean, pressurized water to all fixtures and appliances within your home, while the DWV system’s main function is to safely remove wastewater and expel sewer gases. Both systems are equally important, and a problem in either can disrupt daily life and cause costly damage.
The Water Supply System
The water supply system is the lifeline for all your domestic water needs. It starts with the main water line, which brings water from either a municipal supply or a private well directly into your home. At the entry point, you will typically find a main shut-off valve. This valve is an essential safety feature because it gives you immediate control to stop water flow in the event of an emergency, such as a burst pipe or major leak.
Once inside, water travels through a network of pipes and fittings made from different materials, each suited to its environment and purpose. Pipes are routed throughout walls, floors, and ceilings, branching off to supply kitchens, bathrooms, laundry areas, and other fixtures. Water is delivered under pressure, which is crucial for consistent flow across multiple fixtures. Regularly check tunnels and joints for leaks, as unnoticed drips can erode foundations or foster mold growth.
Key Components of the Water Supply System
- Main Water Line: Connects your home to the city water supply or a well.
- Shut-Off Valves: Installed before major fixtures and appliances to allow easy isolation during repairs.
- Pipes and Fittings: Vary by material and diameter to suit location and pressure needs, distributing water throughout your home efficiently.
It is important to properly insulate pipes to prevent freezing in cold climates. Additionally, regular inspections can help identify leaks early and reduce the risk of water damage or wasted water from unnoticed drips.
The Drain-Waste-Vent (DWV) System
Your DWV system is responsible for carrying wastewater from sinks, toilets, showers, and appliances, and for keeping potentially dangerous sewer gases out of the living spaces. This system does not rely on pressure; instead, it uses gravity and a series of carefully angled pipes to move waste away from fixtures and out to the municipal sewer or septic tank.
Traps are a critical part of the DWV system. These U-shaped sections of pipe are found beneath most sinks and are designed to hold a small amount of water, which acts as a barrier, preventing sewer gases from rising into your home. Vent pipes extend upward through the roof, allowing air to enter the system and enabling smooth drainage by equalizing pressure.
Core Elements of the DWV System
- Drain Pipes: Direct wastewater away from fixtures toward the external sewer or septic lines.
- Traps: Block sewer gases while still allowing waste and water to pass through.
- Vent Pipes: Ensure clean airflow and proper draining, keeping air pressure balanced and helping waste flow efficiently.
Recognizing slow drainage or persistent odors can help catch blockages or vent problems early before they develop into bigger plumbing emergencies.
Common Plumbing Materials
The choice of plumbing materials can influence both the installation process and long-term durability. Modern systems use a combination of PEX, CPVC, and copper pipes, depending on the application and budget.
- PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene):Popular for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to scaling and chlorine, PEX is easier to install and often used in remodels or new construction.
- CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride): Suited for both hot and cold water, CPVC is corrosion-resistant and ideal for homes where water quality may cause rust or scale in traditional pipes.
- Copper: Known for its reliability and longevity, copper is a higher-end choice but requires skill to install and can be more expensive than alternatives.
Choosing materials that best suit your needs can ensure a trouble-free plumbing experience and save you money on repairs or replacements later.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Proactive care is the most effective way to avoid major plumbing disasters. A scheduled maintenance routine can help you monitor the health of your plumbing and detect signs of trouble early.
- Inspect for Leaks: Check under sinks, behind appliances, and in basements for unexplained moisture or pooling water.
- Clean Drains: Install guards in sinks and tubs to prevent hair, soap, and debris from clogging pipes, and never pour grease down the kitchen drain.
- Test Water Pressure: Use a pressure gauge to ensure water pressure remains between 40 and 60 psi—anything higher can strain pipes and fixtures, increasing the risk of leaks.
Paying attention to these routine checks can help reduce the need for emergency repairs and extend the overall life of your plumbing system.
When to Call a Professional
While minor leaks or clogs may be managed with DIY tools and techniques, there are situations where a licensed plumber is necessary. Persistent leaks that do not respond to your efforts, stubborn blockages, or unexplained drops in water pressure often point to underlying issues within the plumbing system. Attempting to resolve these problems without the right expertise can sometimes lead to more damage or higher repair costs.
- Persistent Leaks: Even small leaks may indicate faulty pipes or connections within walls or beneath floors.
- Major Blockages: Clogs that resist plunging or chemical treatments may require professional tools and expertise.
- Low Water Pressure: Sudden pressure drops can indicate pipe corrosion or a significant hidden leak—call a professional to investigate safely and quickly.
Timely intervention by a qualified plumber can help prevent minor issues from becoming major disasters, protecting your home investment and your family’s safety.
Final Thoughts
Knowledge is power when it comes to home ownership, and understanding your plumbing system is crucial. Recognizing how your water supply and DWV systems work, familiarizing yourself with common materials, and sticking to a regular maintenance schedule will protect your home against many common headaches. When in doubt, do not hesitate to reach out to trusted professionals for help or advice; your peace of mind and your house depend on it.